Planetary Nebula
RA 17h 58m 33s.42 Dec +66° 37' 59".5
Draco
3,000 light-years (1,000 parsecs)
1.2 arcminutes (1.2 light-years or 0.35 parsecs) wide.
ACS/WFC
September 18, 1994
J.P. Harrington and K.J. Borkowski, and NASA
January 11, 1995
Links
to other images in the series:
Jan 1995 Jan
2001 Sept 2004 July
2008 Oct 2012
ABOUT THIS IMAGE:
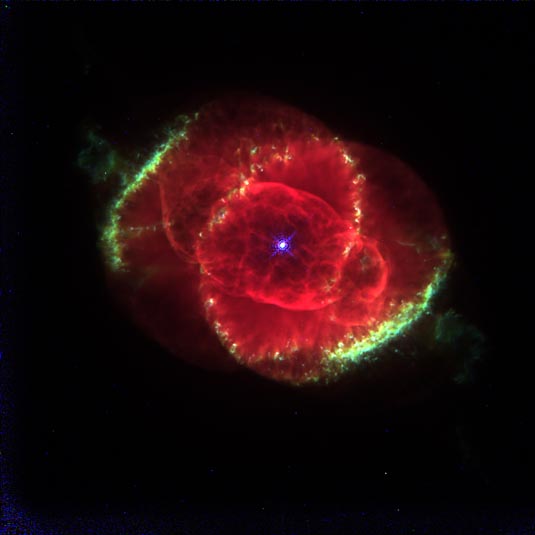
This NASA Hubble Space Telescope image shows one of the most complex planetary nebulae ever seen, NGC 6543, nicknamed the "Cat's Eye Nebula." Hubble reveals surprisingly intricate structures including concentric gas shells, jets of high-speed gas and unusual shock-induced knots of gas. Estimated to be 1,000 years old, the nebula is a visual "fossil record" of the dynamics and late evolution of a dying star.
A preliminary interpretation suggests that the star might be a double-star system. The dynamical effects of two stars orbiting one another most easily explains the intricate structures, which are much more complicated than features seen in most planetary nebulae. (The two stars are too close together to be individually resolved by Hubble, and instead, appear as a single point of light at the center of the nebula.)
According to this model, a fast "stellar wind" of gas blown off the central star created the elongated shell of dense, glowing gas. This structure is embedded inside two larger lobes of gas blown off the star at an earlier phase. These lobes are "pinched" by a ring of denser gas, presumably ejected along the orbital plane of the binary companion.
The suspected companion star also might be responsible for a pair of high- speed jets of gas that lie at right angles to this equatorial ring. If the companion were pulling in material from a neighboring star, jets escaping along the companion's rotation axis could be produced.
These jets would explain several puzzling features along the periphery of the gas lobes. Like a stream of water hitting a sand pile, the jets compress gas ahead of them, creating the "curlicue" features and bright arcs near the outer edge of the lobes. The twin jets are now pointing in different directions than these features. This suggests the jets are wobbling, or precessing, and turning on and off episodically.
This color picture, taken with the Wide Field Planetary Camera-2, is a composite of three images taken at different wavelengths. (red, hydrogen-alpha; blue, neutral oxygen, 6300 angstroms; green, ionized nitrogen, 6584 angstroms). The image was taken on September 18, 1994. NGC 6543 is 3,000 light-years away in the northern constellation Draco.
The term planetary nebula is a misnomer; dying stars create these cocoons when they lose outer layers of gas. The process has nothing to do with planet formation, which is predicted to happen early in a star's life.